map的底层实现
map 示例:
先来看一个demo, 打印maps的指针地址:
1 | package main |
打印结果为:
1 | maps init p(0x1160948) |
由此可见,传入函数内部的map指针发生了变化,所以map的传参方式为值传递。我们修改为以下demo,并修改maps中name的值,看是否为影响原始maps。
1 | package main |
打印结果为:
1 | maps init p(0x1160948) |
可见传参之后,在函数内的修改影响到了外部全局变量的maps。
golang源码解析
Golang中map的底层实现是一个散列表,在这个散列表中,主要有两个结构体,一个叫hmap(a header for a go map),一个叫bucket(bmap)。
hmap 结构
1 | // A header for a Go map. |
Golang的map中用于存储的key/value结构是bucket数组。而bucket(即bmap)的结构如下:
1 | // A bucket for a Go map. |
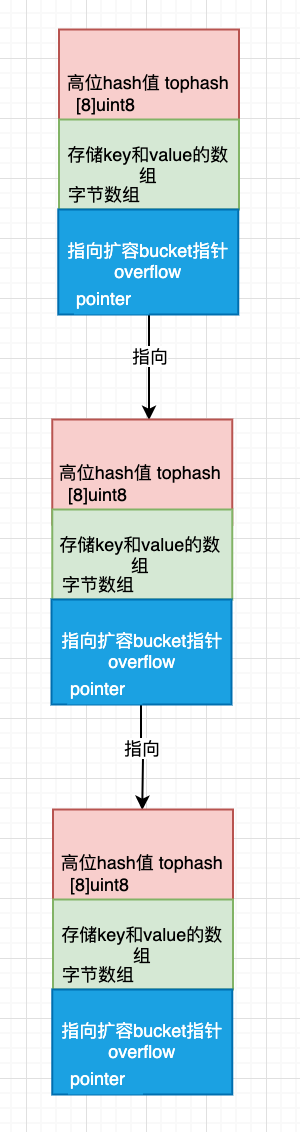
bmap就是我们所说的桶bucket,实际上就是每个bucket固定包含8个key和value(可以查看源码bucketCnt=8).实现上面是一个固定的大小连续内存块,分成四部分:
- 每个条目的状态
- 8个key值
- 8个value值
- 指向下个bucket的指针
桶里面会最多装 8 个key,这些key之所以会落入同一个桶,是因为它们经过哈希计算后,哈希结果是“一类”的。在桶内,又会根据 key 计算出来的 hash 值的高 8 位来决定 key 到底落入桶内的哪个位置(一个桶内最多有8个位置)。
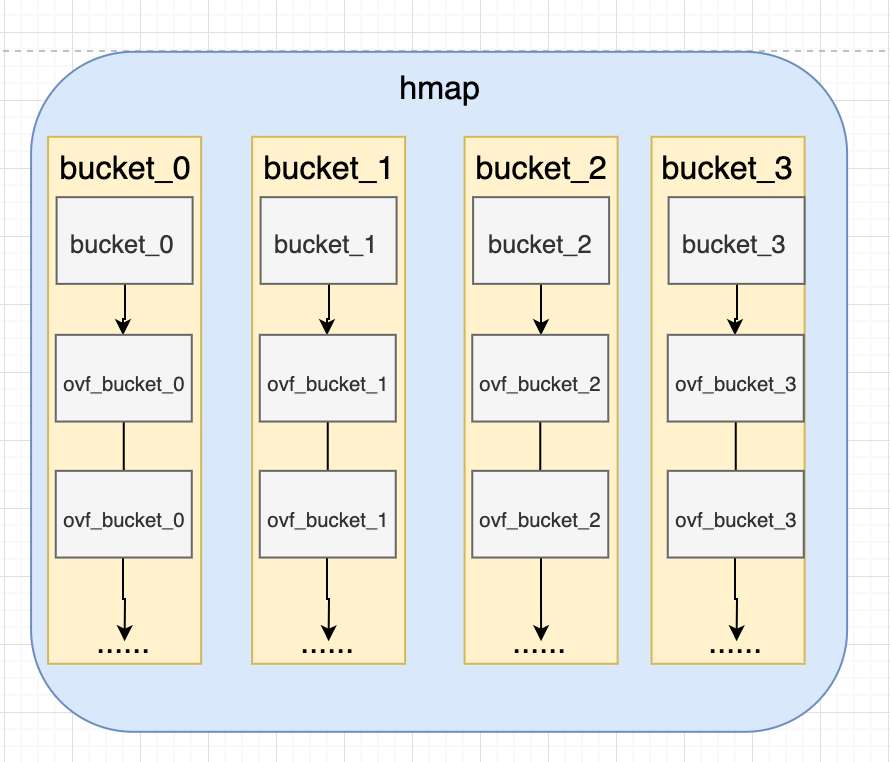
如果超过 8key-value对,将继续额外的bucket,并通过overflow指针连接。当哈希表增大到一定长度时,会分配一个新数组,桶的两倍大。 桶是递增的,从旧桶数组复制到新桶数组。
具体结构如下:
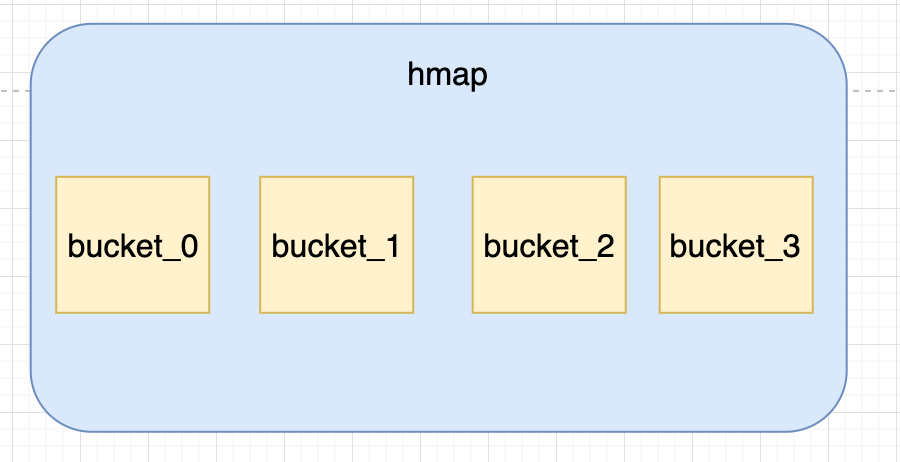
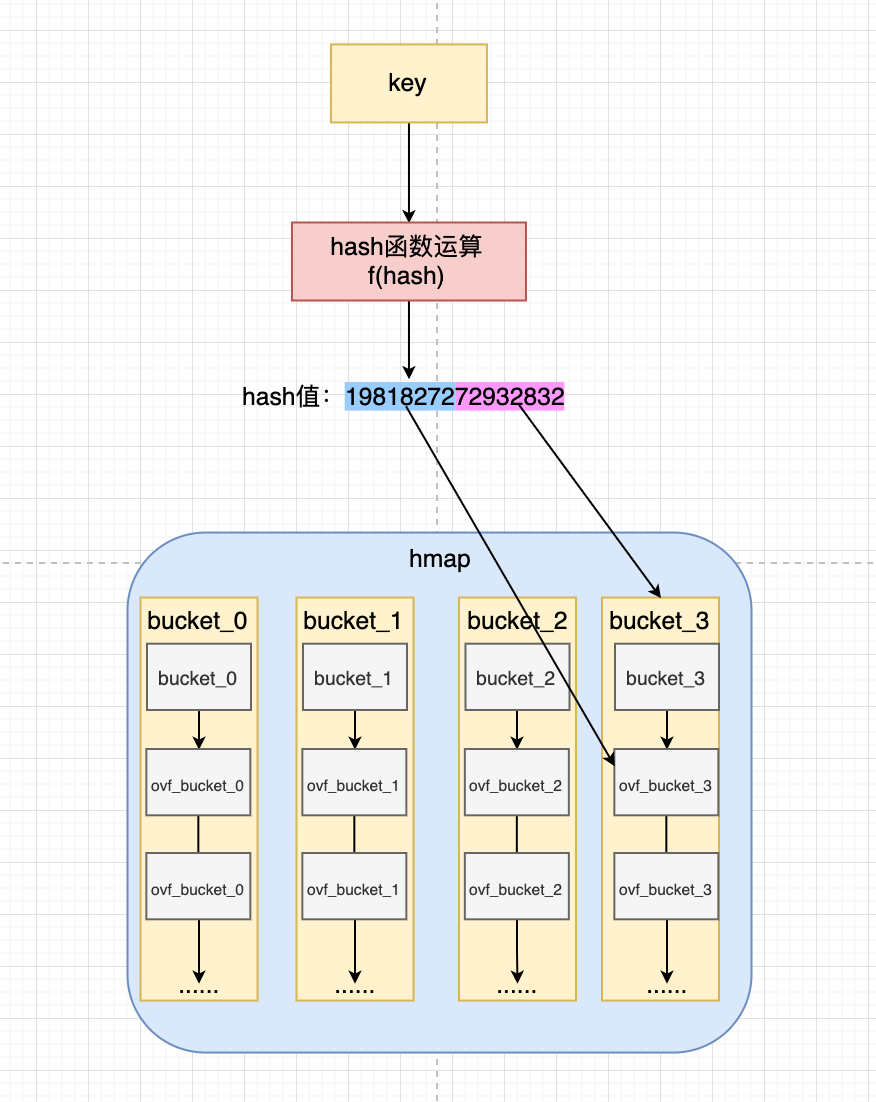
通过hmap的定义可知道,一个map会有多个bucket,而hmap通过buckets指针指向真正buckets结构,如下图所示:
而bucket又通过一个扩展字段组成了一个链表结构,所以,整体的结构如下:
哈希表的特点是会有一个哈希函数,对传来的key进行哈希运算,得到唯一的值,一般情况下都是一个数值。Golang的map中也有这么一个哈希函数,也会算出唯一的值。
Golang把求得的值按照用途一分为二:高位和低位。
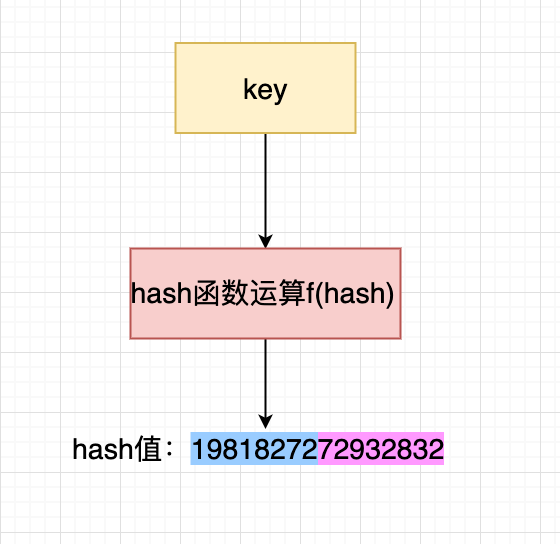
如图所示,蓝色为高位,红色为低位。
然后低位用于寻找当前key属于hmap中的哪个bucket,而高位用于寻找bucket中的哪个key。上文中提到:bucket中有个属性字段是“高位哈希值”数组,这里存的就是蓝色的高位值,用来声明当前bucket中有哪些“key”,便于搜索查找。
需要特别指出的一点是:我们map中的key/value值都是存到同一个数组中的。数组中的顺序是这样的:
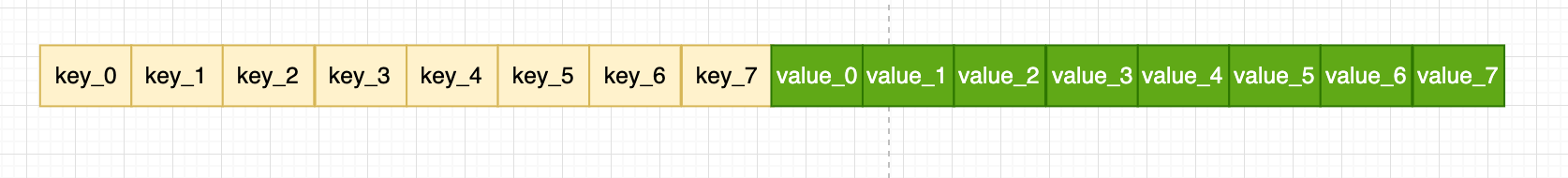
并不是key0/value0/key1/value1的形式,这样做的好处是:在key和value的长度不同的时候,可以消除padding带来的空间浪费。
至此map对整个结构图如下所示:
tophash分析
tophash是一个长度为8的数组,它不仅仅用来存放key的哈希高8位,在不同场景下它还可以标记迁移状态,bucket是否为空等。
tophash值含义
当tophash对应的K/V被使用时,存的是key的哈希值的高8位;当tophash对应的K/V未被使用时,存的是K/V对应位置的状态。
1 | emptyRest = 0 |
当tophash[i] < 5时,表示存的是状态;
当tophash[i] >= 5时,表示存的是哈希值;
emptyRest
这个值有两层意思:一是表示该tophash对应的K/V位置是可用的;二是表示该位置后面的K/V位置都是可用的。
赋值:
- 初始化的时,tophash会被置为emptyRest。
- 删除map元素时,会判断是否需要把删除key对应的tophash置为emptyRest。
emptyOne
仅表示该tophash对应的K/V位置是可用的,其后面的是否可用不知道。
赋值:
删除map元素时,会把key对应的tophash先置为emptyOne,再继续判断是否需要置为emptyRest。
demo问题
通过map源码分析可知,虽然map参数传递时为值传递,但底层通过一个buckets指针指向了一个真正的buckets结构,即使map拷贝了一份,但buckets指针指向但仍然是同一个底层结构,所以,改变map中的key时,会影响到全局的map。